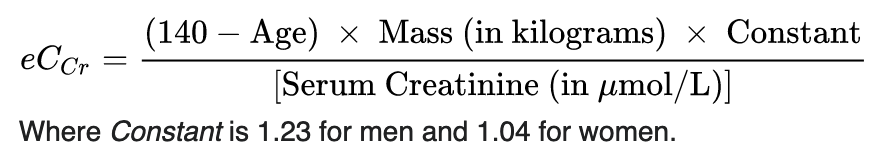
Vancomycin exerts its antibacterial activity by inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis, a process that is time-dependent (time>MIC). Protein binding is moderate (~50%) and penetration of the drug into the lung and CNS is poor.
The usual dose is 1000 mg (for a 70 kg patient) or 10-15 mg/kg Actual Body Weight rounded to the nearest 250 mg, including obese patients or patients < 50kg. For obese patients can consider adjusted body weight dosing based on height and weight. Maximum dose is 2 g.
A loading dose of 20 mg/kg Actual Body Weight maybe considered in patients who are critically ill and where serious MRSA infection is suspected.
| Actual Body Weight (kg) | Initial Dose (mg) | Infusion Time (min) |
|---|---|---|
| Less than 60 | 1000 | 60 |
| 60-70 | 1250 | 90 |
| 71-80 | 1500 | 120 |
| 81-90 | 1750 | 120 |
| Greater than 90 | 2000 | 120 |
| Actual Body Weight (kg) | Initial Dose (mg) | Infusion Time (min) |
|---|---|---|
| Less than 60 | 750 | 60 |
| 60-70 | 1000 | 60 |
| 71-80 | 1250 | 90 |
| 81-90 | 1500 | 90 |
| Greater than 90 | 1750 | 120 |
The initial dosing interval for all patients (empiric treatment and serious gram-positive infections) is based on estimated creatinine clearance using the Cockcroft-Gault equation:
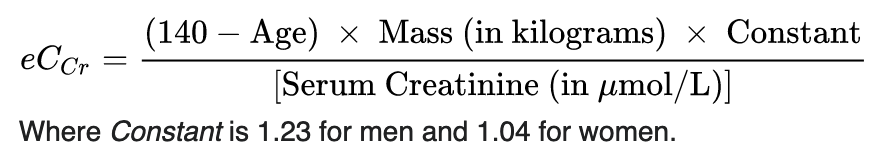
| Creatinine Clearance (mL/min) | Dosing Interval* |
|---|---|
| ≥50 | q12h |
| 10-49 | q24-36h |
| <10 | q48h |
| Hemodialysis (IHD/SLED) | Consult Pharmacy |
| CVVHD | q24h |
These are initial recommendations only and assume relatively stable renal function. Use clinical judgement and account for patient’s clinical status and severity of infection. Dose and dosing interval should be adjusted based on trough levels.
Baseline and twice weekly while on vancomycin.
The risk of nephrotoxicity during vancomycin monotherapy is < 10% when trough concentrations are maintained ≤ 15 mg/L. The incidence of nephrotoxicity is ~10-20% for patients with trough levels maintained between 15-20 mg/L.
The risk of nephrotoxicity is further increased if any of the following apply:
duration of therapy exceeds 14 days
the dose per day exceeds 4 g
trough vancomycin levels are maintained above 20 mg/L
potentially nephrotoxic agents are being used concomitantly – aminoglycosides, amphotericin B, cisplatin, diuretics, NSAIDs, or radiocontrast dye
Peak levels are no longer routinely performed due to lack of evidence correlating efficacy and toxicity.
Trough level should normally be drawn at steady state and should be obtained 30 minutes prior to the next scheduled dose (i.e. pre-4th dose in patients with normal renal function).
In patients receiving IHD/SLED levels are drawn pre-hemodialysis either before session or with AM labs on days of scheduled session.
Duration of treatment expected to be a minimum of 5 days.
If duration of treatment is greater than 7 days, recheck level weekly as vancomycin may accumulate.
Treatment of serious or deep-seated infections that may require more aggressive dosing.
For safety, in patients at risk of nephrotoxicity: concurrent nephrotoxic medications, pre-existing or unstable renal function, age greater than 60, or extremes of weight (under 50 or over 100 kg).
There is no definitive evidence that supports a relationship between trough concentrations and organism eradication or overall patient outcome. The following recommendations are based on pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of vancomycin.
| Indications | Target Trough (mg/L) |
|---|---|
| Most indications | 8-15 |
Serious or deep-seated Gram-positive infections:
|
12-18 (Note: more aggressive dosing with trough targets >15 must be balanced with the risk of acute kidney injury which is associated with higher trough concentrations) |
IHD/SLED
|
15-20 |
Rybak MJ, Le J, Lodise TP, Levine DP, Bradley JS, Liu C, Mueller BA, Pai MP, Wong-Beringer A, Rotschafer JC, Rodvold KA, Maples HD, Lomaestro B. Therapeutic Monitoring of Vancomycin for Serious Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus Infections: A Revised Consensus Guideline and Review by the American Society of Health-system Pharmacists, the Infectious Diseases Society of America, the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society, and the Society of Infectious Diseases Pharmacists. Clin Infect Dis. 2020;71(6):1361-1364.
Dalton BR, Rajakumar I, Langevin A, Ondro C, Sabuda D, Griener TP, Dersch-Mills D, Rennert-May E. Vancomycin area under the curve to minimum inhibitory concentration ratio predicting clinical outcome: a systematic review and meta-analysis with pooled sensitivity and specificity. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020;26(4):436-446.
Stewart JJ, Jorgensen SC, Dresser LD, et al. A Canadian perspective on the revised 2020 ASHP/IDSA/PIDS/SIDP guidelines for vancomycin AUC-based therapeutic drug monitoring for serious MRSA infections. J Assoc Med Microbiol Infect Dis.2020;6(1):3-9.
van Hal SJ, Paterson DL, Lodise TP. Systematic review and meta-analysis of vancomycin-induced nephrotoxicity associated with dosing schedules that maintain troughs between 15 and 20 milligrams per liter. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013;57(2):734-44.
Chavada R, Ghosh N, Sandaradura I, Maley M, Van Hal SJ. Establishment of an AUC0-24 threshold for nephrotoxicity is a step towards individualized vancomycin dosing for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017;61(5):e02535-16.
Sunnybrook Antimicrobial Handbook (accessed through Metrodis Jan 2023).
UHN Antimicrobial Stewardship Program: Vancomycin Dosing and Monitoring Guidelines (May 2018)