DISCLAIMER: Consider consulting ID or ASP before ordering aminoglycosides.
Aminoglycosides are indicated in the treatment of infections due to Gram-negative aerobic bacilli, bacterial endocarditis in combination with other agents and surgical prophylaxis in combination with other agents. Tobramycin is the NH aminoglycoside of choice as levels are done in-house allowing for rapid availability of results for appropriate monitoring and dosage adjustments.
Toxicity associated with aminoglycosides includes nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity. Nephrotoxicity may be associated with elevated trough levels and is thought to be reduced by extended interval dosing. Aminoglycoside therapy may affect cochlear and/or vestibular function. Ototoxicity is not associated with either peak or trough aminoglycoside levels.
Note: Neonatal and pediatric patients are excluded from these guidelines. Physicians are encouraged to order aminoglycosides based on published Hospital for Sick Children’s guidelines.
Extended interval aminoglycoside dosing (EIAD) is preferred over conventional dosing in patients that meet EIAD criteria. (See algorithm for aminoglycoside dosing.) The use of EIAD produces higher serum peak concentrations which optimizes bacterial killing. Drug related toxicity may also be decreased as EIAD results in an “aminoglycoside-free” period where accumulation of the aminoglycoside in tissues such as the kidney or inner ear may be reduced. Other advantages include convenience and reduced costs for monitoring, drug administration and preparation.
Conventional aminoglycoside dosing uses reduced doses at more frequent intervals to achieve target peak and trough levels.
Aminoglycoside synergy dosing involves the use of low dose gentamicin in combination with an antimicrobial agent that has activity against the cell wall of Gram-positive bacteria (such as β-lactams or vancomycin) in the treatment of Gram-positive infections.
Initial aminoglycoside dosing is determined based on ideal body weight (IBW) and creatinine clearance (CrCl).
CrClmale = ((140 − age) × weight [kg] × 1.2)/(serum creatinine [μmol ∖ /L] )
CrClfemale = 0.85 × CrClmale
IBWmale = 50 kg + 2.3 × (inches over 5 feet)
IBWfemale = 45 kg + 2.3 × (inches over 5 feet)
If actual body weight (ABW) is less than IBW, use ABW
If ABW > IBW + 30%, use adjusted body weight (AdjBW)
AdjBW = [(actual body weight - IBW) x 0.4] + IBW
Conventional dosing is recommended only in the following situations:
Renal dysfunction with CrCl less than 40 mL/min
Septic shock
Age less than 18 years
Pregnancy
Osteomyelitis, endocarditis, or meningitis (when used for synergy)
Ascites
Burns
Cystic fibrosis
For all other patients, extended interval dosing is recommended.
Dosing can be determined by using CrCl to determine the dosing interval (see table 1) or the Hartford nomogram
Use IBW to determine dose
Use actual body weight if less than IBW
Use adjusted body weight if actual body weight is greater than IBW + 30%
Round dose to nearest 20mg increment for tobramycin or gentamicin and to the nearest 50mg increment for amikacin
EIAD using CrCl to Determine Interval
| CrCl (mL/min) | Tobramycin and Gentamicin Dose1,2 | Amikacin Dose1,2 |
|---|---|---|
| ≥60 | 4-7 mg/kg q24h | 15m/kg q24h |
| 40-59 | 4-7 mg/kg q36h | 15mg/kg q36h |
EIAD dosing is based on the Hartford Nomogram
***Only applicable for 7 mg/kg of tobramycin or gentamicin, or 15 mg/kg of amikacin – plotting doses lower or higher than 7 mg/kg or 15 mg/kg respectively, may under or overestimate clearance
Initial level testing: Single aminoglycoside serum level drawn 8 to 12 hours after the first dose
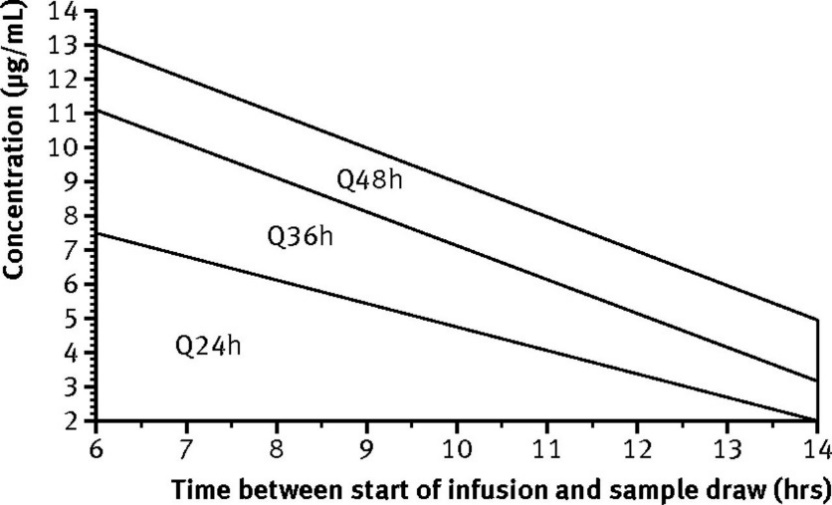
The appropriateness of the EIAD frequency will be assessed by plotting the exact time and value of the 8 to 12 hour post-dose level on the nomogram below.
Tobramycin/gentamicin (7 mg/kg/dose): Plot level on graph
Amikacin (15 mg/kg/dose): Divide level in half, then plot on graph
Adjust based on nomogram
Below nomogram (< 2 mg/L) 🡪 give dose once daily
Q24H, Q36H, or Q48H region 🡪 give dose at indicated interval
Above nomogram 🡪 discontinue EIAD and switch to conventional dosing

Serum creatinine should be drawn at baseline and every 3 days while on AMG.
Monitor urine output q24h while on AMG.
Baseline auditory testing should be done for patients with baseline auditory deficiencies and any patients expected to be on greater than 7 days of therapy.
Serum AMG levels are NOT to be routinely drawn. Criteria for AMG levels are:
Expected duration of treatment > 3-5 days (i.e. documented infection). Obtain a trough level by day 7 of therapy and then weekly for duration of therapy. Troughs are drawn immediately prior to the dose.
Use of Hartford nomogram to assess appropriateness of EIAD frequency. Level should be drawn 8 to 12 hours after the first dose.
Renal function borderline (i.e. CrCl = 40-60 mL/min or in elderly patients) or fluctuating
Concurrent use of nephrotoxic drugs.
If trough level is greater than 1.0 mg/L, re-assess need for AMG. Converting to conventional dosing may be required.
Target Trough Levels for EIAD
| Aminoglycoside | Desired Trough (mg/mL) |
|---|---|
| tobramycin | less than 0.5 |
| gentamicin | less than 0.5 |
| amikacin | less than 1 |
Use IBW to determine dose
Use actual body weight if less than IBW
Use adjusted body weight if actual body weight is greater than IBW + 30%
Round dose to nearest 20mg increment for tobramycin or gentamicin and the nearest 50mg increment for amikacin
Recommended Dose for Conventional Dosing
| CrCl (mL/min) | Tobramycin & Gentamicin in Severe Infections | Tobramycin & Gentamicin in Mild-to-Moderate Infections | Gentamicin for Synergy in Gram-Positive Infections | Amikacin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| > 70 | 2 mg/kg Q8H | 1.5 mg/kg Q8H | 1 mg/kg Q8H | 7.5 mg/kg Q12H |
| 40 - 69 | 2 mg/kg Q12H | 1.5 mg/kg Q12H | 1 mg/kg Q12H | 7.5 mg/kg Q12H |
| 20 - 39 | 2 mg/kg Q24H | 1.5 mg/kg Q24H | 1 mg/kg Q24H | 7.5 mg/kg Q24H |
| < 20 | 2 mg/kg, then draw level in 24h to determine interval | 1.5 mg/kg, then draw level in 24h to determine interval | 1 mg/kg, then draw level in 24h to determine interval | 7.5 mg/kg Q24H, then draw level in 24 h to determine interval |
| Hemodialysis | 2 mg/kg Q48-72H, re-dose when pre-HD level less than 3-5mg/L | 1.5 mg/kg Q48-72H, re-dose when pre-HD level less than 2-3 mg/L | 1 mg/kg Q48-72H, re-dose when pre-HD level less than 1mg/L | 7.5 mg/kg Q24-72H, re-dose when pre HD level less than 10mg/L |
| CRRT | 2 mg/kg Q24-48H | 1.5 mg/kg Q24-48H | 1 mg/kg Q24-48H | 10 mg/kg, then 7.5 mg/kg Q24-48H |
Serum creatinine should be drawn at baseline and every 3 days while on AMG.
Serum AMG levels may be drawn as pre and post after the third or fourth regular dose, as long as a steady state is reached.
Troughs are drawn immediately prior to the dose and peaks are drawn 30 minutes after completion of the infusion.
Obtain a set of peak and trough levels every 7 days during therapy or if renal function changed.
Guidelines for Desired Serum Concentrations in Conventional Dosing
| Infection | Tobramycin and Gentamicin | Amikacin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trough (mg/L) | Peak (mg/L) | Trough (mg/L) | Peak (mg/L) | |
| Urinary tract infections | less than 2 | 4 - 6 | Less than 5 | 15 - 20 |
| Serious infections (bacteremia, pneumonia, sepsis, cellulitis, wound) | less than 2 | 6 – 10 | less than 10 | 20 - 25 |
| Life-threatening infections (e.g. P. aeruginosa pneumonia) | less than 2 | 8-10 | less than 10 | 25 - 30 |
| Synergy in gram positive infections | less than 1 | 3 - 5 | NA | NA |
Dipiro JT et al. Concepts in Clinical Pharmacokinetics, 4th Edition.
Nicolau D, Quintilani R, Nightingale C. Once daily aminoglycosides. Conn Med 1992;56:561-63.
Nicolau D et al. Experience with a once-daily aminoglycoside program administered to 2 184 adult patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1995;39(3):650-55.
Hatala R, Dinh T, Coddk DJ. Once-daily aminoglycoside dosing in immunocompetent adults: a meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 1996;124(8):717-25.
Freeman C et al. Once-daily dosing of aminoglycosides: review and recommendations for clinical practice. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1997;39(6):677-86.
Lexicomp. Gentamicin (systemic), Tobramycin (systemic), Amikacin: Drug Information. (accessed via UpToDate Sep 2022).
Sunnybrook Antimicrobial Handbook (accessed via Metrodis Jan 2023).
Stanford Health Care Aminoglycoside Dosing Guide (accessed Jan 2023).